Gut microflora is affected by DON
The study revealed that DON can cause intestinal flora imbalance. DON increased the relative abundance of Firmicutes and decreased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes, resulting in a significant increase in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in pigs (Fig. 1F). A high ratio of Firmicutes/ Bacteroidetes has been associated with diarrhea. DON also significantly decreased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria in broiler intestines (Fig. 1E). In addition, Prevotella abundance decreased, and Prevotella is beneficial for intestinal homeostasis and health.
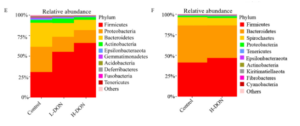
Figure 1: Mean plasma concentration of DON-3S, the main metabolite of DON, after single oral administration of DON (0.5 mg/kg PV).
It is suggested that the changes observed in the intestinal microflora are mainly related to DON-induced changes in the metabolism and digestive function of the animals.. Finally, the patterns observed in the gut of broilers and pigs showed both similarities and differences. This may be linked to the intensity of DON-induced toxicity in each species.
Reference: Jia B., Lin H., Yu S., Liu N., Yu D., Wu A., 2023. deoxynivalenol induces disorders of the intestinal flora, dysfunctions and lesions of the organs in broilers and pigs. J Hazard Mater. 451 ; 131172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131172