January 21, 2024
Reading Time: 2 minutes
In this Myco’News, we spotlight recent findings on deoxynivalenol (DON) posing significant threats to dairy cow health, rumen function, and milk production. Here are the three main insights from recent research done in vivo in China:
Disruption of rumen function and microbiota
DON contamination in feed significantly disrupts rumen fermentation. It reduces volatile fatty acids (VFAs) such as propionate and butyrate, which are essential for energy production in ruminants. Moreover, DON alters the microbial ecosystem in the rumen, decreasing beneficial bacteria like Lachnospiraceae and Butyrivibrio. These disturbances reduce nutrient digestion efficiency and ultimately affect milk yield.
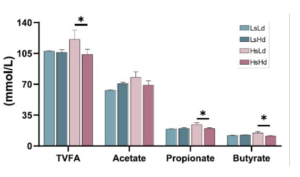
Figure 1. Total volatile fatty acid (TVFA), acetate, propionate and butyrate production of cows expose to low (L; 20.8%) and high (H; 27.8%) levels of starch (s); and low (L; 0.34 ppm) and high (H; 3.09 ppm) of DON (d).
Diet matters: High-starch risks
High level of starch in the TMRs exacerbate the negative effects of DON. These diets promote rumen acidosis, increasing microbial imbalance and reducing DON detoxification capacity. High-starch, DON-contaminated diets led to a sharp decline in milk yield and increased oxidative stress compared to low-starch TMRs.
Health Implications and Prevention
Beyond production losses, DON elevates oxidative stress indicators (ROS) and inflammation markers (TNF-α, IL-1β and IFN-γ). The immune response of cows was also negatively affected by DON, increasing IgG and complement 4 (C4).
Effective strategies to mitigate DON impact include optimizing feed composition, regularly monitoring DON contamination levels in feeds, and incorporate a detoxifier. Maintaining a balanced diet, especially one lower in starch, is essential for reducing the severity of DON effects on rumen health and overall cow well-being.
Reference: Dong J., Zhao Z., Wang Z., Li S., Zhang Y., Sun Z., Qin G., Zhang X., Zhao W. Demelash N., Wang T. and Zhen Y. 2024. Impact of deoxynivalenol on rumen function, production, and health of dairy cows: Insights from metabolomics and microbiota analysis. Journal of Hazardoud Materials, 465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.133376